This lecture covers querying the blog database with joins. Our blog database is designed, created, and populated. Now we get to the payoff: asking complex questions and getting answers by joining the tables together.
Query 1: List All Posts with Their Author’s Name
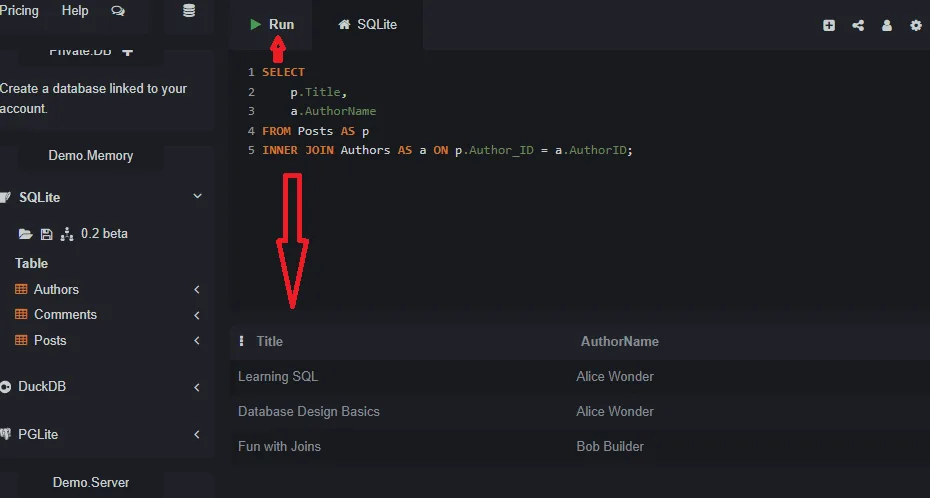
This is a fundamental query. We want to see the title of each post and the name of the person who wrote it. This requires a simple INNER JOIN between the `Posts` and `Authors` tables.
SELECT
p.Title,
a.AuthorName
FROM Posts AS p
INNER JOIN Authors AS a ON p.Author_ID = a.AuthorID;This query links each post to its author and displays the relevant information together.
Query 2: List All Comments for a Specific Post
Let’s find all the comments for the first post, “Learning SQL”. We’ll need to join `Posts` and `Comments`. We can filter using a WHERE clause on the post’s title.
SELECT
c.CommenterName,
c.CommentContent
FROM Comments AS c
INNER JOIN Posts AS p ON c.Post_ID = p.PostID
WHERE p.Title = 'Learning SQL';Query 3: A Complex, Three-Table Join
Now for the ultimate query: let’s list all comments and include both the post title and the post’s author. This requires us to join all three tables together!
SELECT
p.Title, -- From the Posts table
a.AuthorName, -- From the Authors table
c.CommenterName, -- From the Comments table
c.CommentContent -- From the Comments table
FROM Comments AS c
INNER JOIN Posts AS p ON c.Post_ID = p.PostID
INNER JOIN Authors AS a ON p.Author_ID = a.AuthorID;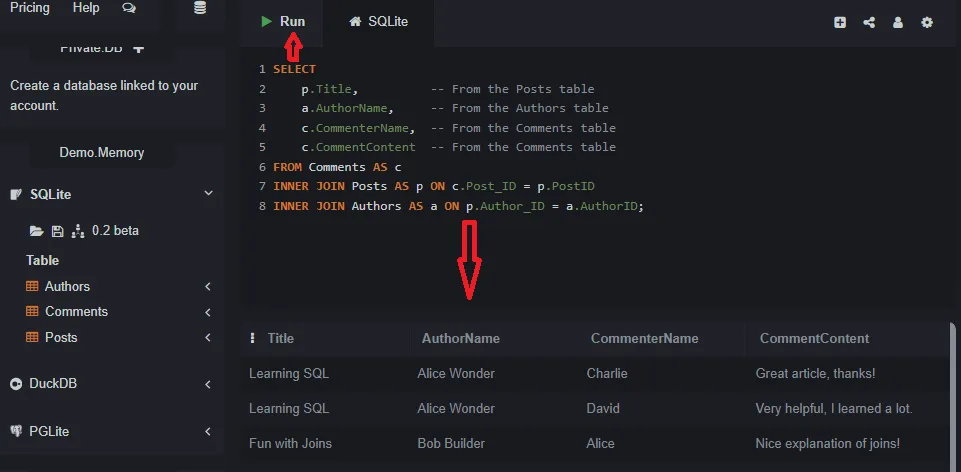
Here, we are chaining our joins. We join `Comments` to `Posts`, and then we join that result to `Authors`. The database is smart enough to figure out these relationships and give us a single, unified result.
Query 4: List All Posts That Have No Comments
How can we find which articles haven’t received any feedback? This is a perfect job for a LEFT JOIN. We will list all posts and see where the comment information is NULL.
SELECT
p.Title
FROM Posts AS p
LEFT JOIN Comments AS c ON p.PostID = c.Post_ID
WHERE c.CommentID IS NULL;This should return “Database Design Basics”, our only post without comments.
In the Next Lecture…
We will continue our journey into shaping data by looking at how to combine the results of multiple `SELECT` statements using `UNION` and `UNION ALL`.